Featured
About SMOS

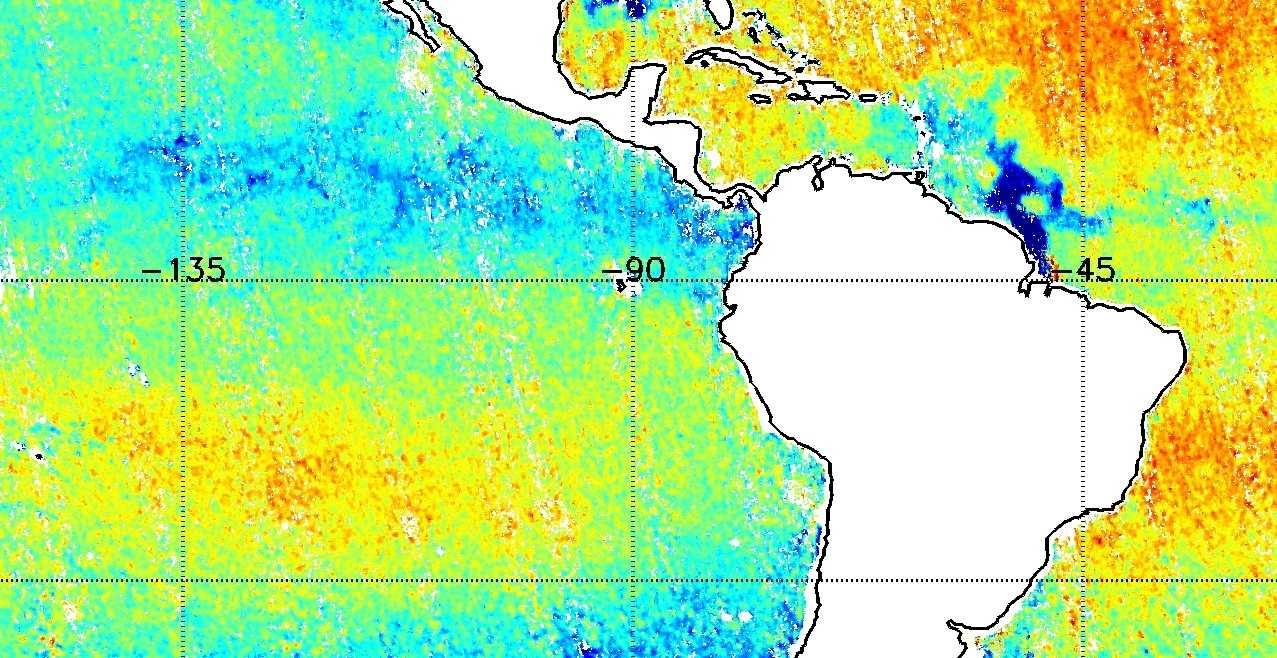
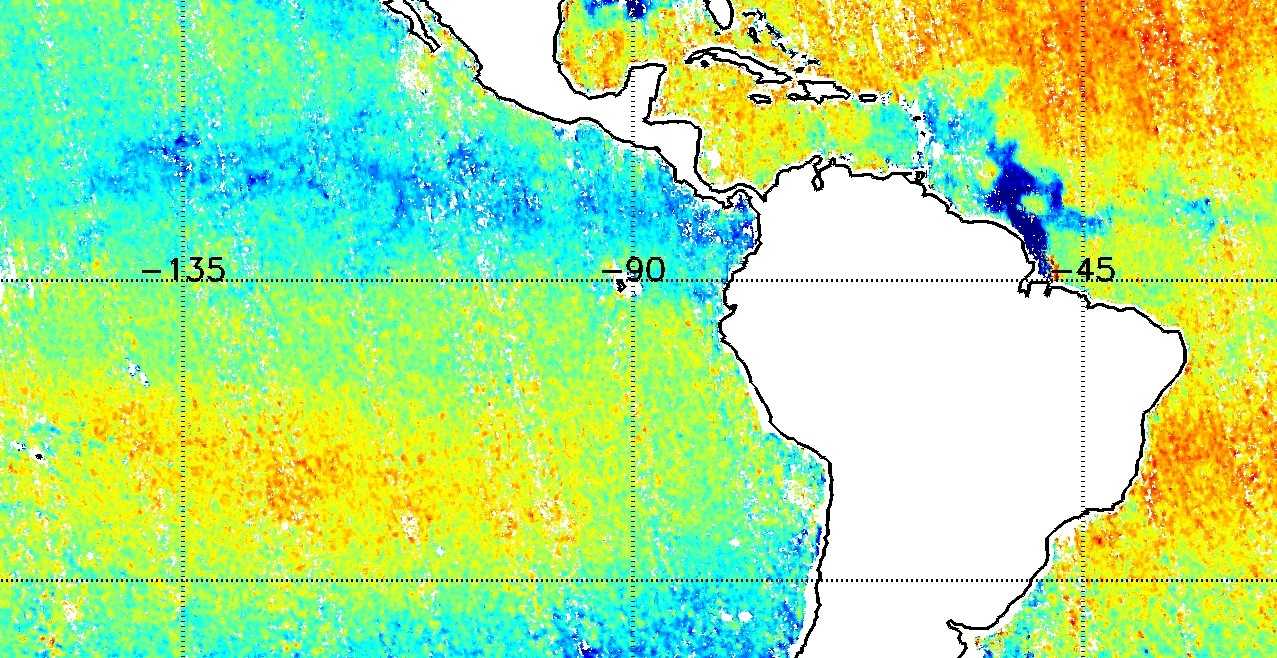
The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission, launched on 2 November 2009, is one of the European Space Agency's Earth Explorer missions, which form the science and research element of the Living Planet Programme.
It is the first mission to provide, from microwave L-band measurements, global observations of variability in soil moisture and sea surface salinity due to continuous exchange in Earth's water cycle between the oceans, the atmosphere and the land. These key geophysical parameters, soil moisture for hydrology studies and salinity for enhanced understanding of ocean circulation, are both vital for climate change models.
Although designed as a five-year mission, the Programme Board for Earth Observation has approved the extension of SMOS mission operations based on its excellent technical and scientific performance until the end of 2025. This enables enhanced analysis of longer-term process and new synergistic opportunities from new observing systems.
| Orbit Altitude | Min 761.3 km Max 788.4 km (height of elliptical orbit) |
| Orbit Type | LEO, sun-synchronous, polar, circular, dawn-dusk (LTAN 06:00) |
| Orbit Inclination | 98.42° |
| Repeat Cycle | 149 days, 18 days sub-cycle |
SMOS Objectives
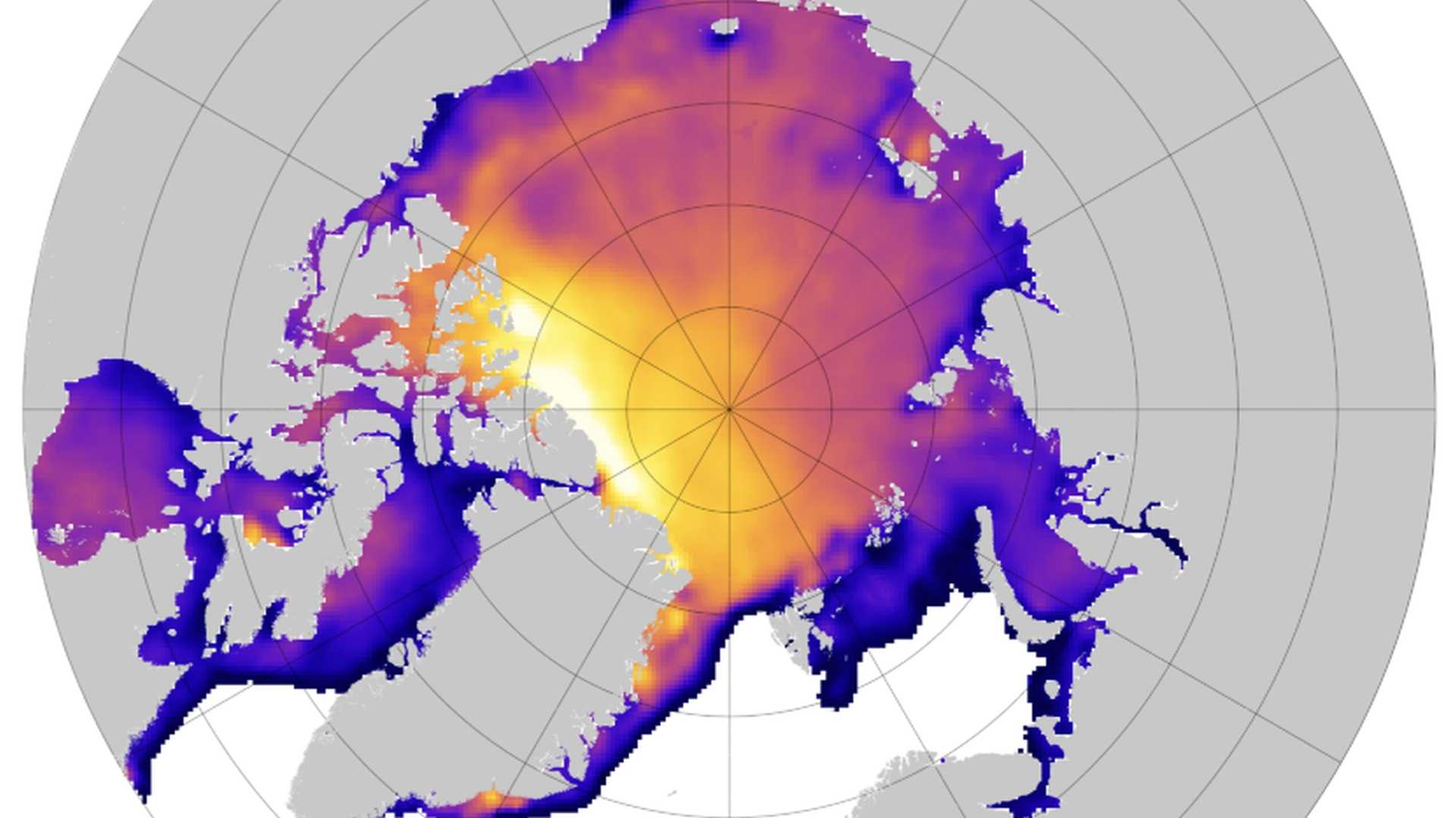
The SMOS mission furthers our scientific knowledge of the Earth's water cycle, contributes to better weather and extreme-event forecasting, and helps improve climate models. SMOS also contributes significant information to cryospheric research.
SMOS Instruments

find out more